Not Above Equilibrium Price Is A Price Floor

Types of price floors.
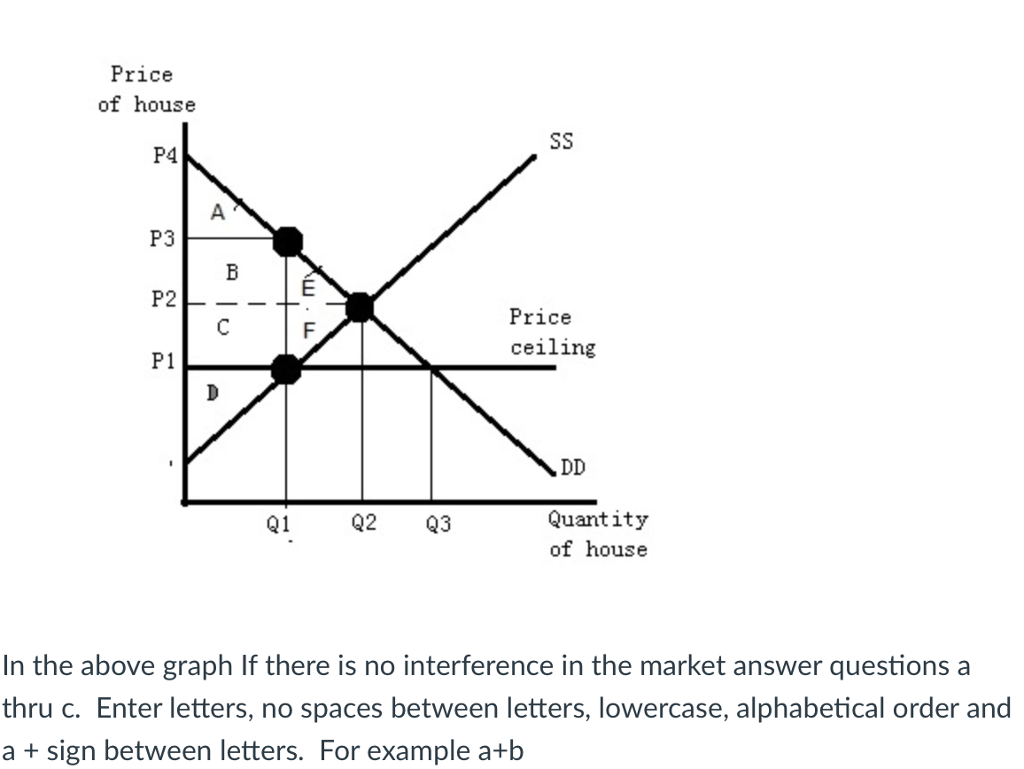
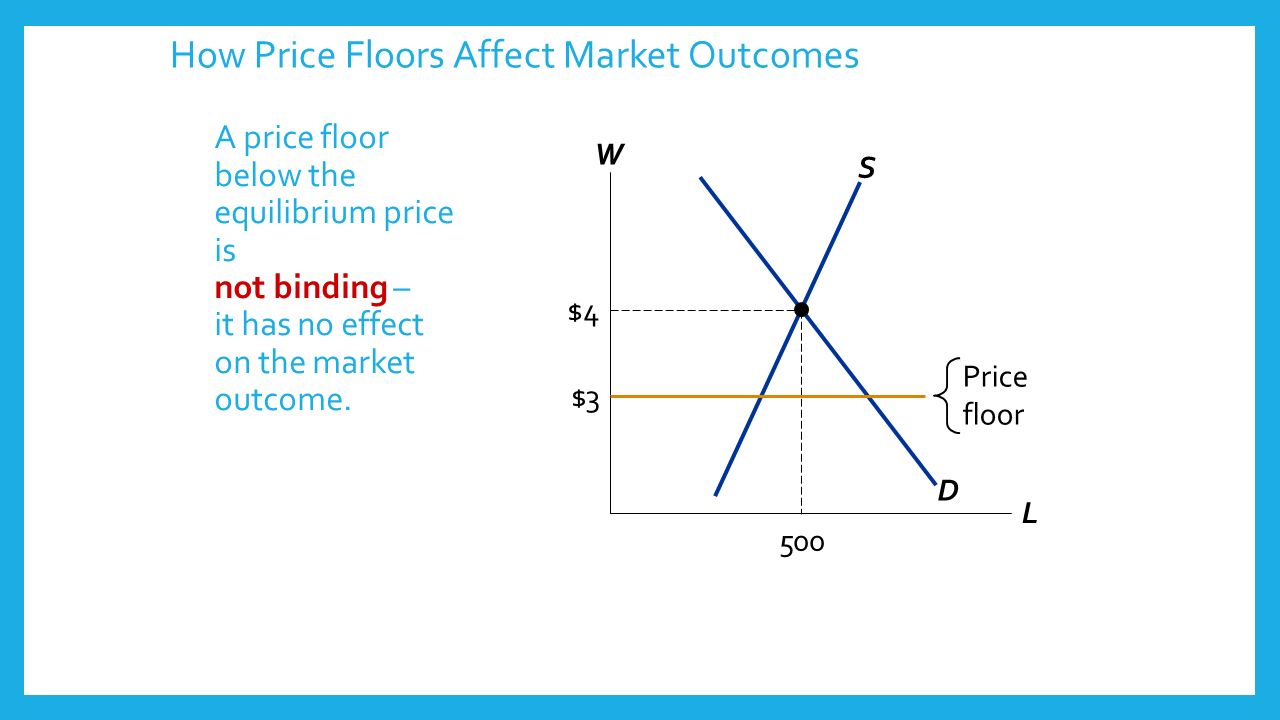
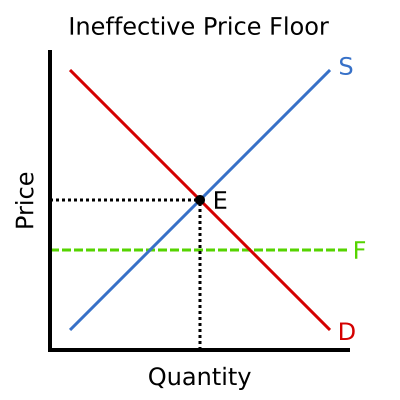
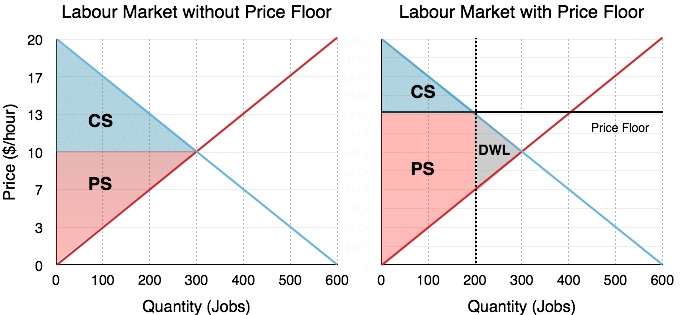
Not above equilibrium price is a price floor. When a price floor is set above the equilibrium price as in this example it is considered a binding price floor. If a price floor is not binding then the equilibrium price is above the price floor. By increasing the price the quantity demanded will fall and the quantity supplied will rise. It has no legal enforcement mechanism.
How does a price floor set above the equilibrium level affect quantity demanded and quantity supplied. A price floor is a government or group imposed price control or limit on how low a price can be charged for a product good commodity or service. The equilibrium price is above the price floor. Suppose the equilibrium price of a tube of toothpaste is 2 and the government imposes a price floor of 3 per tube.
The equilibrium price commonly called the market price is the price where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external. This graph shows a price floor at 3 00. More than one of the above is correct. A price floor set above the equilibrium is an attempt to make the price higher.
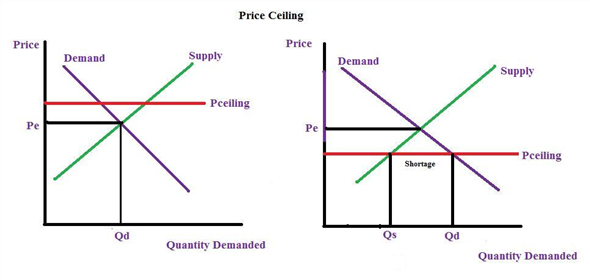
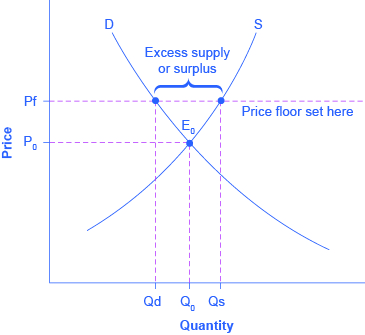
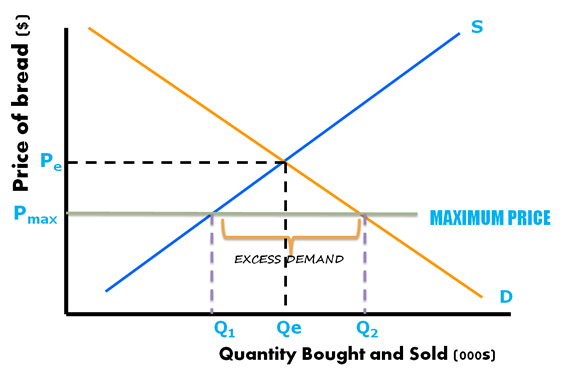
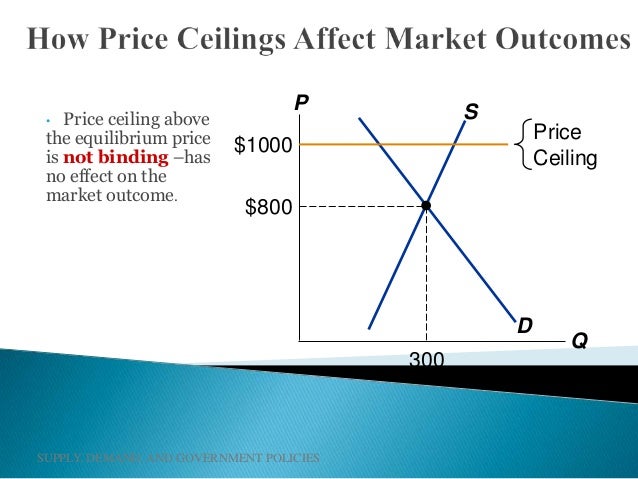
Drawing a price floor is simple. The result is a quantity supplied in excess of the quantity demanded qd. A price ceiling is a maximum amount mandated by law that a seller can charge for a product or service. It s generally applied to consumer staples.
At higher market price producers increase their supply. The equilibrium price is below the price floor. Simply draw a straight horizontal line at the price floor level. That will create a surplus.
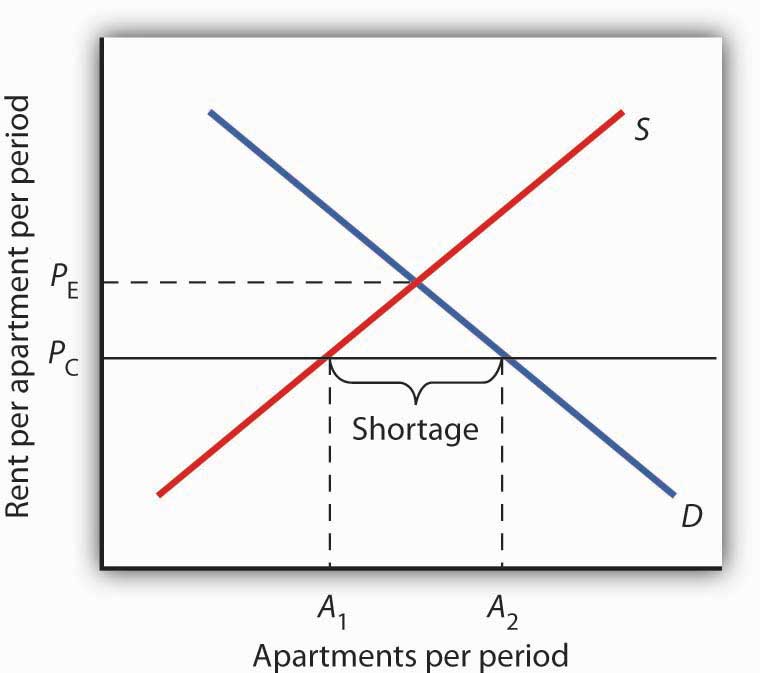
The equilibrium price is below the price floor. There will be a surplus in the market. If a price floor is not binding then a. There will be a shortage in the market.
But if price floor is set above market equilibrium price immediate supply surplus can be observed. If a price floor is set above the equilibrium price in a market multiple choice o rationing will be unnecessary. A binding price floor is one that is greater than the equilibrium market price. O shortages will develop the quantity demanded will exceed the quantity supplied.
When quantity supplied exceeds quantity demanded a surplus exists. A price floor must be higher than the equilibrium price in order to be effective. The quantity supplied will exceed the quantity demanded. In contrast consumers demand for the commodity will decrease and supply surplus is generated.
If it s not above equilibrium then the market won t sell below equilibrium and the price floor will be irrelevant.