Nucleophilic Substitution At Vinylic Carbon

The interesting thing about these compounds is the carbon halogen bond and all the nucleophilic substitution.
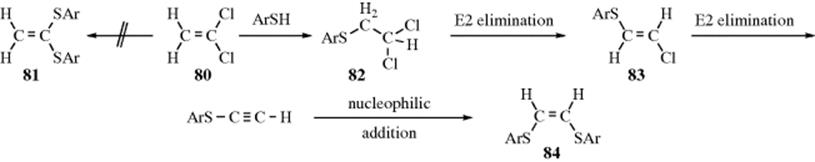
Nucleophilic substitution at vinylic carbon. Nucleophilic vinylic substitutions are closely related to nucleophilic aromatic substitutions as in both the leaving group leaves from an unsaturated carbon atom. The two main mechanisms are the s n 1 reaction and the s n 2 reaction. Joong youn shim phillip f. In 1935 edward d.
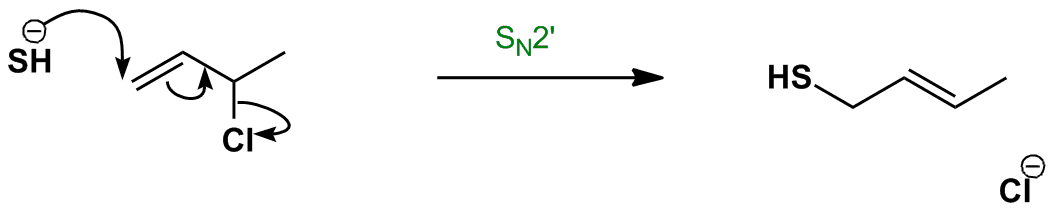
Both of these mechanisms are impossible at a saturated substrate. E2 elimination will dominate. An allylic rearrangement or allylic shift is an organic reaction in which the double bond in an allyl chemical compound shifts to the next carbon atom. Factors conducive to the energetic preference for the in plane sn2 pathway.
1 for such a concerted bimolecular nucleophilic substitution at a vinylic sp 2 carbon are proposed two possible mechanisms namely in plane. S n 2 substitution. Journal of the american chemical society 2001 123 24 5787 5793. The most common mechanisms are the tetrahedral mechanism and the closely related addition elimination mechanism.
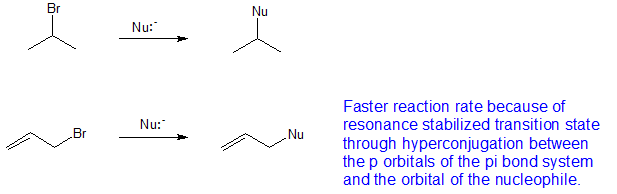
In reaction conditions that favor a s n 1 reaction mechanism the intermediate is a carbocation for which several resonance structures are possible. Journal of the american chemical society 2000 122 10 2294 2299. S stands for chemical substitution n stands for nucleophilic and the number represents. Vinyl c x bond x halogen oxygen nitogen is stronger than the alkyl c x bond because of a resonance interaction.
Hughes and sir christopher ingold studied nucleophilic substitution reactions of alkyl halides and related compounds. Nucleophilic substitution at a vinylic carbon 252 is difficult see sec. N s o secondary r 2 ch s n 2 substitution and or e2 elimination depending on the basicity of the nucleophile. Halogenoalkanes also known as haloalkanes or alkyl halides are compounds containing a halogen atom fluorine chlorine bromine or iodine joined to one or more carbon atoms in a chain.
It is encountered in nucleophilic substitution. They proposed that there were two main mechanisms at work both of them competing with each other. However the vinylic substitution routes are much more diverse and disclose more of the details of the reaction. Nucleophilic substitution at unactivated vinylic carbon.
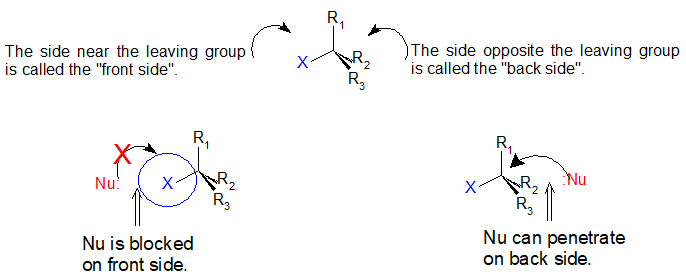
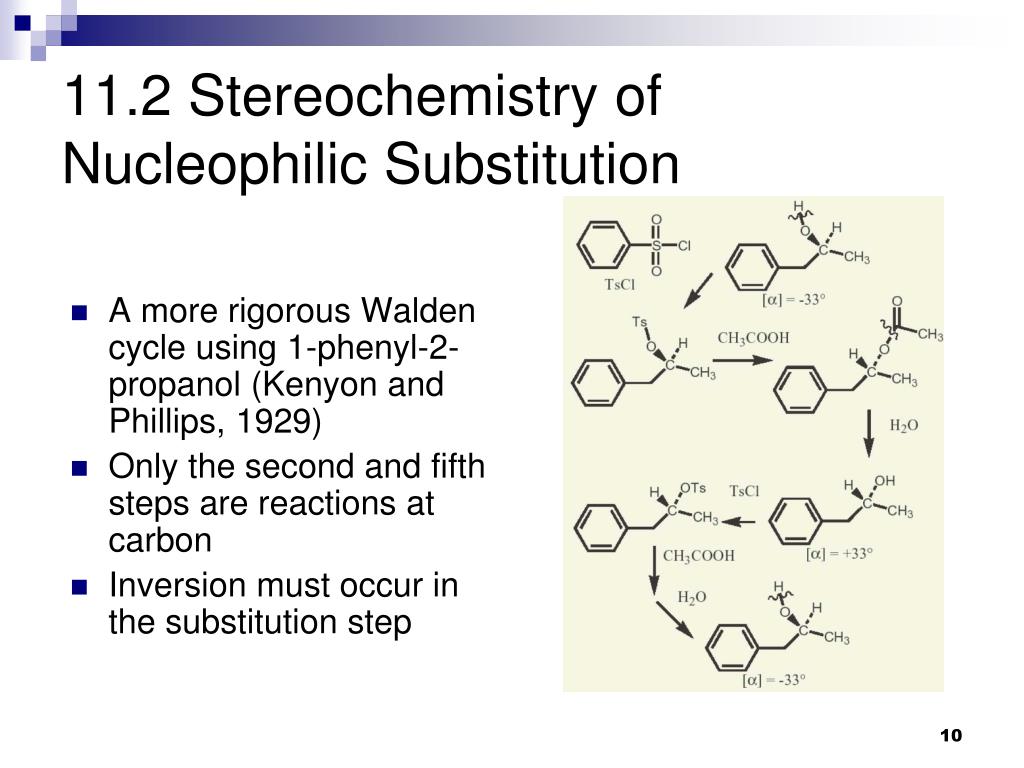
Boone and ann m. Bases weaker than acetate pk a 4 8 give less elimination. Concerted nucleophilic substitution at an sp 3 carbon typically bimolecular nucleophilic substitution s n 2 reaction is one of the most fundamental reactions in organic chemistry giving a substitution product with inversion of the configuration. Inversion versus retention of configuration for nucleophilic substitution at vinylic carbon.
10 g i but many examples are known. This explains the product distribution or.