Ocean Floor Features Turbidity

He reason the deposit on the bottom forms the way it does is a result of.
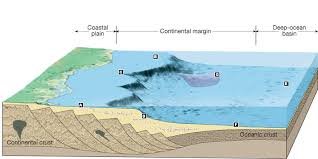
Ocean floor features turbidity. Effect on ocean floor. The assertion and the reason are both correct and. A turbidity current is the downslope movement of dense sediment laden water created when sand and mud on the continental shelf and slope are dislodged and thrown into suspension. Ocean geologic features 45 there are vast hydrate deposits below 1 000 meters along the us east coast.
Slumping of large masses of sediment creates a dense slurry which. Few abyssal plains are located in the pacific ocean because turbidity currents only occur along passive continental margins. Abyssal hills or seaknolls oceanic trenches oceanic ridges seamounts. The gas hydrate beds leak gas es into the water forming cold seeps on the ocean floor.
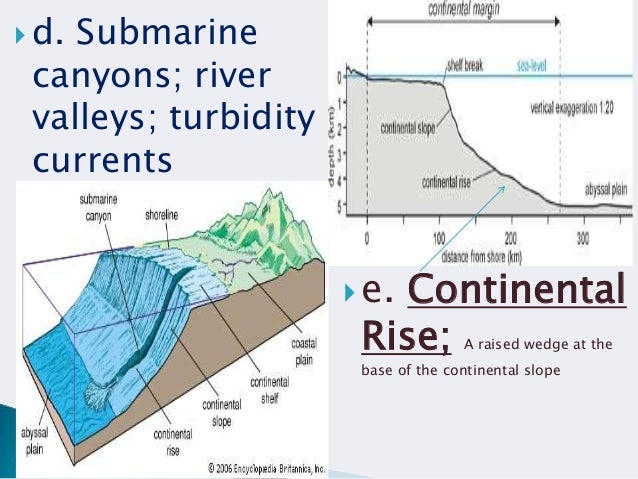
What are three. Large and fast moving turbidity currents can incise and erode continental margins and cause damage to artificial structures such as telecommunication cables on the seafloor understanding where turbidity currents flow on the ocean floor can help to decrease the amount of damage to telecommunication cables by avoiding these areas or reinforcing the cables in vulnerable areas. Turbidity current underwater density current of abrasive sediments. Turbidity currents are erosive to the continental slope and as a result carve out submarine canyons.
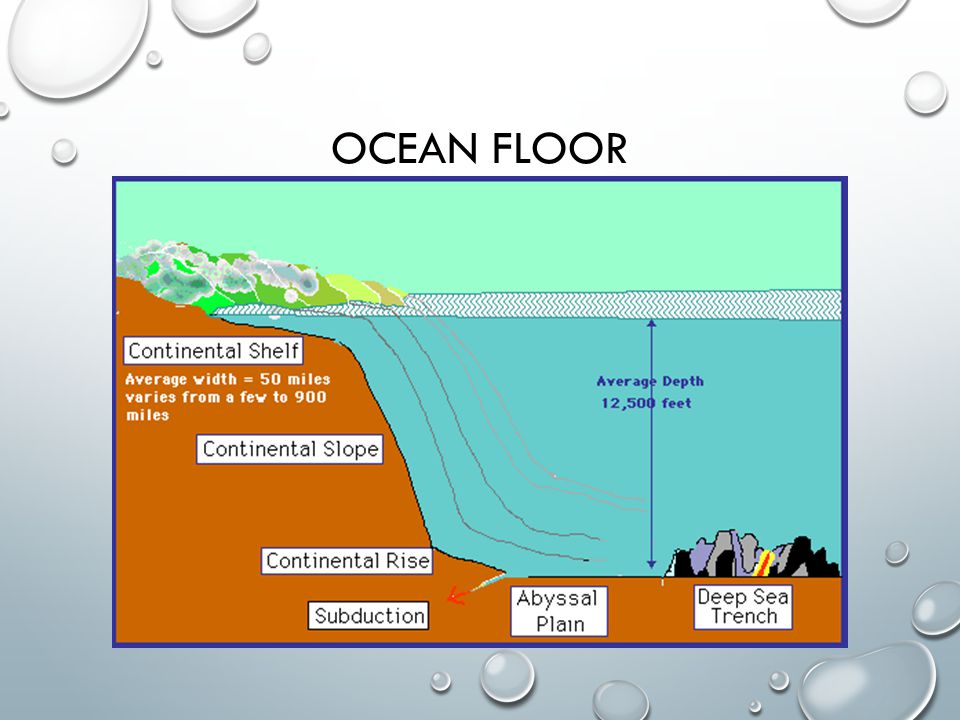
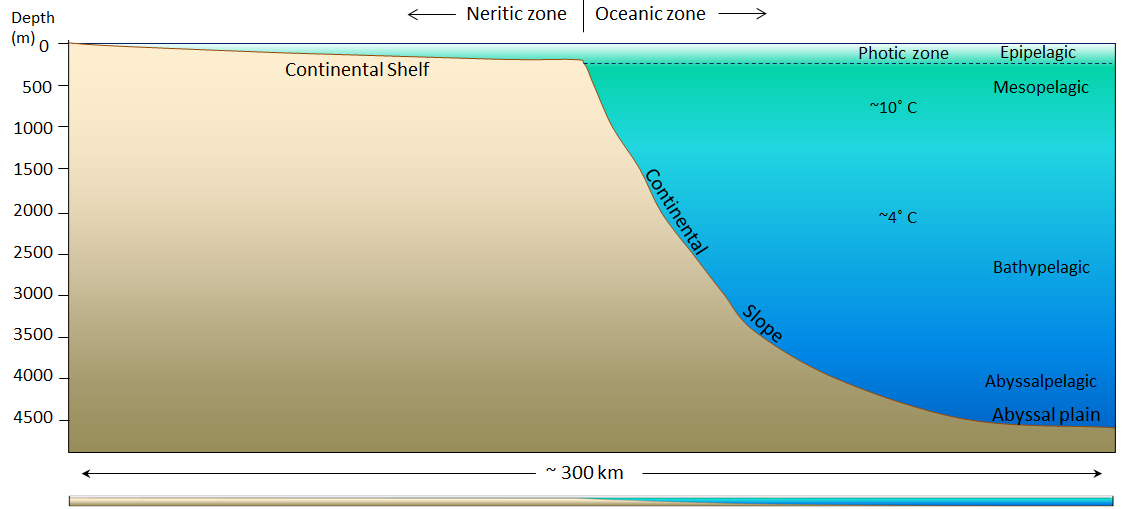
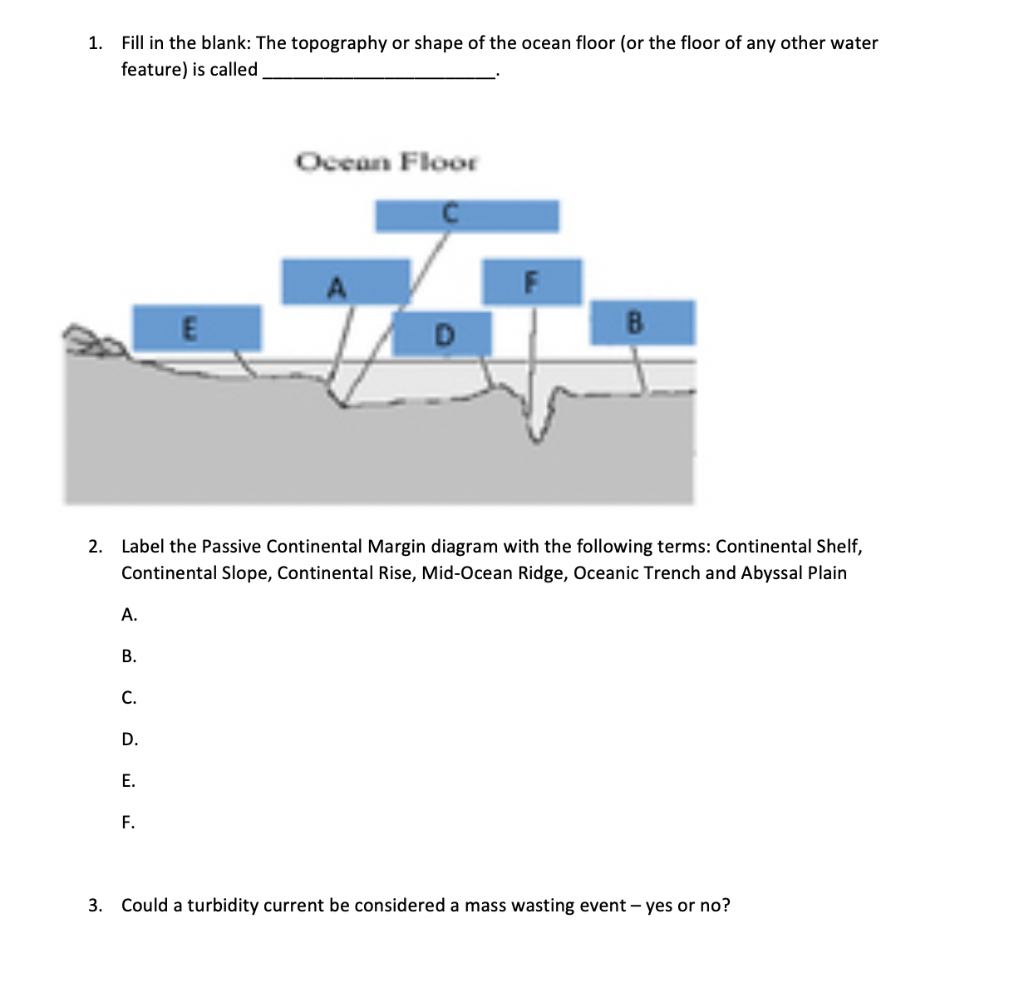
Most ocean floor features owe their origins to. A mid ocean ridge is found near the center of most ocean basins. The ocean floor is called the abyssal plain. Features rising up from the ocean floor include seamounts volcanic islands and the mid oceanic ridges and rises.
Seamounts rise more than a kilometer from the ocean floor and are remnants of oceanic ridge volcanoes. The sediments that make up abyssal plains are carried there by turbidity currents or deposited as a result suspended sediments settling. As the turbidity of water increases it becomes denser and less clear due to a higher concentration of these light blocking particles. Features of the ocean include the continental shelf slope and rise.
Abyssal plains are deep exteremely flat features. Pacific ocean basin seamounts and guyots are common widespread features of the sea floor. Such currents appear to be relatively short lived transient phenomena that occur at great depths. They are thought to be caused by the slumping of sediment that has piled up at the top of the continental slope particularly at the heads of submarine canyons.
Below the ocean floor there are a few small deeper areas called ocean trenches. Submarine canyons a turbidity current is the. Turbidity is a measure of the level of particles such as sediment plankton or organic by products in a body of water. Seamounts are submerged volcainic peaks that dot the ocean floor.
This hydrocarbon seepage is common on continental margins around the world.