Oil Seeps From Ocean Floor

Or r tracks naturally occurring oil seeps helps distinguish oil seeps from production platform leaks and other spills and works with partners like the u s.
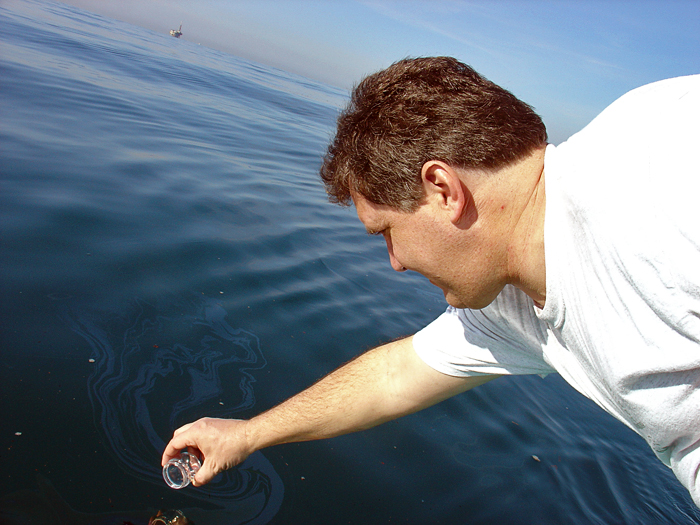
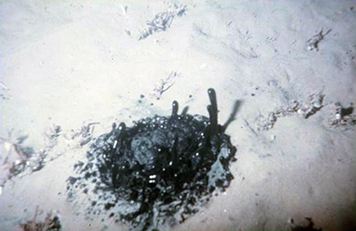
Oil seeps from ocean floor. Even though seeps are not without their own impacts on marine life natural oil seeps release oil slowly over time allowing. Coast guard and the u s. Petroleum literally rock oil is a substance that has formed beneath the surface of the earth over eons. Even though seeps are not without their own impacts on marine life natural oil seeps release oil slowly over time allowing.
The remains of ancient plants and animals have been buried and compressed beneath thousands of feet of sand mud and rock. While the amount of oil and its ultimate fate in such manmade disasters is well known the effect and size of natural oil seeps on the ocean floor is murkier. While not technically oil spills oil seeps from the ocean floor naturally release oil from subterranean reservoirs and represent the largest source of oil entering seas both in the united states and around the world. The waters off southern california are one area in particular which host hundreds of known naturally occurring oil and gas seeps.
The scientists avoided areas with natural oil seeps features in which oil slowly leaks onto the ocean floor through a series of cracks. A new study finds that the natural. Ian macdonald naturally formed oil and methane from the oceanfloor seeps upward into the water column at many points in the sea and partially reaches the water surface. These seeps contribute about 5 million gallons of oil to the ocean annually with.
While not technically oil spills oil seeps from the ocean floor naturally release oil from subterranean reservoirs and represent the largest source of oil entering seas both in the united states and around the world. In the modern era. Noting that dissolved oil could have toxic effects on marine ecosystems wang et al. Investigated the transport and ultimate dissolution of hydrocarbons released from natural seeps in the ocean by.
Originally at the sites of natural seeps and leaks from fissures in the earth s surface. A 2003 report from the national research council estimates that on average approximately 160 000 tonnes of petroleum enter north american waters through natural seeps each year.