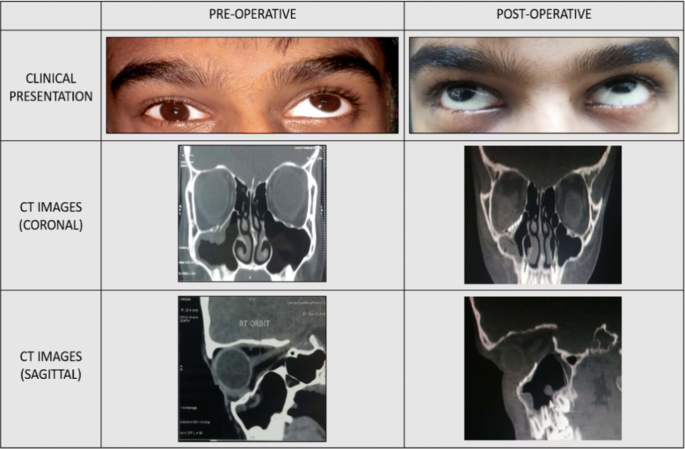
Orbital Floor Fracture In Children
We retrospectively analysed all consecutive children younger than 18 years of age that were referred to the oral.
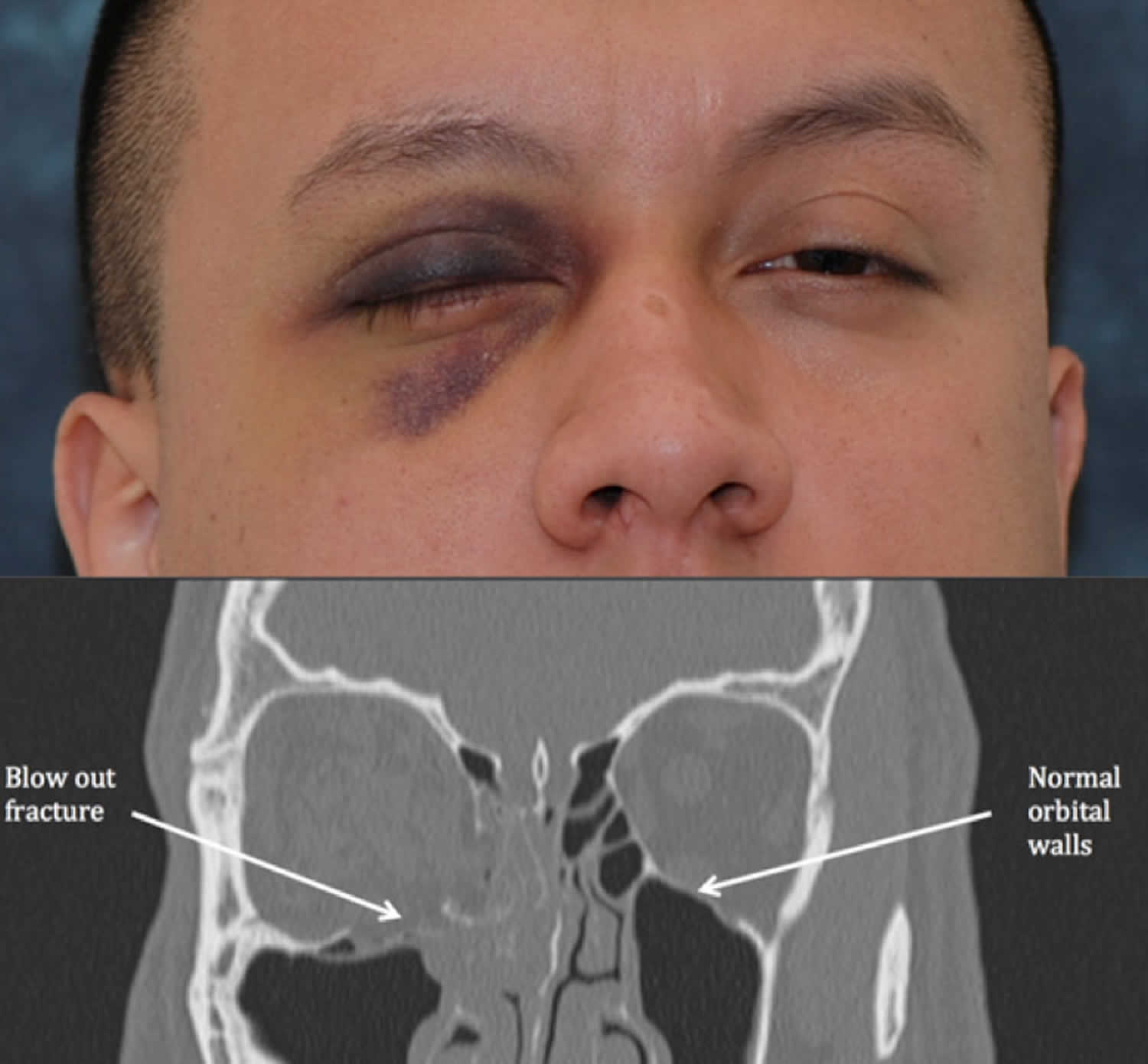
Orbital floor fracture in children. Orbital floor fracture also known as blowout fracture of the orbit. Fractures of the orbital floor are a common result of facial injury and in the adult population the. The most common complaint was double vision 52. Immediately after an.
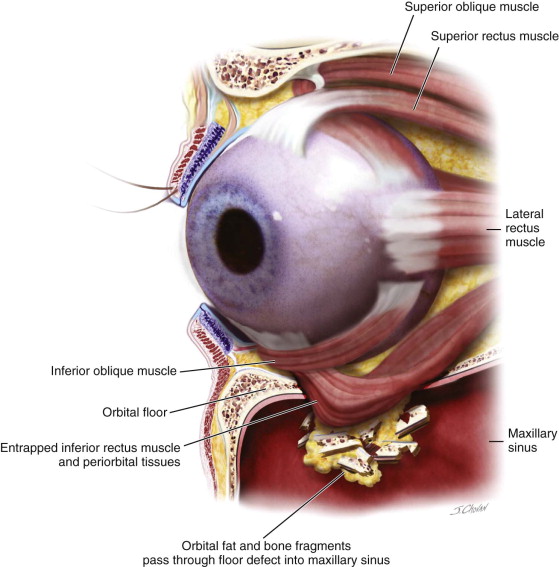
However this injury is relatively uncommon in very young children in whom most orbital fractures involve the roof rather than the orbital floor. Road traffic accidents 18 52 35 were the most common cause with the orbital floor 42 52 81 being the most common fracture site. Fractures of the orbital floor are rare in children under 8 years old but until the age of 9 years they are more likely to involve the anterior orbital floor than the posterior orbital floor as in adults 20 and to be associated with diplopia. Thirty eight patients underwent surgical intervention and extraocular muscle entrapment 56 was the most common indication for surgery.
A review of outcomes introduction. Children are more likely to have isolated linear fractures of the orbital roof similar to the greenstick fractures seen in the orbital floor. The same hydraulic and buckling theories that are associated with the orbital floor and medial walls apply to the orbital roof. This can be explained by anatomic changes.
Noe nasal orbital ethmoidal fractures nasal bone injuries are common in older children and adults and must always be assessed for an underlying noe fracture. In children type of fracture are different from that in adult. Isolated orbital floor fracture. The aetiology of orbital floor fractures in children also differs from the adult population where the most common causes in decreasing frequency are assault falls and traffic accidents.
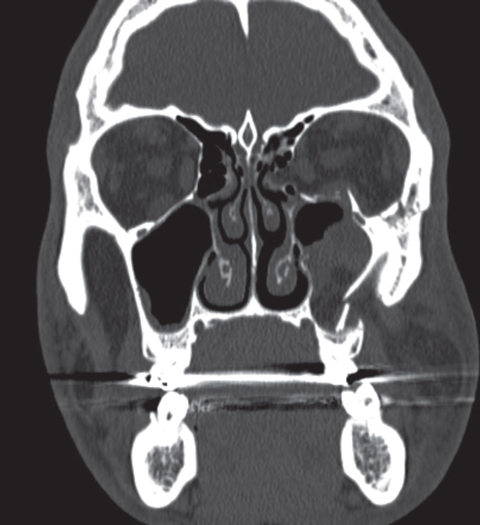
The orbital floor resulted in the blowout fracture. When direct force is applied to the nasal bone it can cause a collapse of the paired nasal lacrimal and ethmoidal bones. Although these two mechanisms are presented as individual concepts it is likely that the wide variety of clinically observed orbital fracture is resulted from a combination of these two mecha nisms 10. In classic indirect blowout fracture also known as orbital hydrostatic theory low velocity blunt force to the soft tissue raises the intraorbital pressure fracturing the thin medial orbital floor figure 2.
In our study sporting injuries and bicycle injuries were the most frequent causes. See orbital floor fractures. Orbital fractures in children. Orbital floor fractures disease entity.








&w=538)