Orbital Floor Fracture Maxillary Nerve

Inferior blowout fractures involving the floor of the orbit maxillary sinus roof are the most common followed by medial wall blowout fractures.
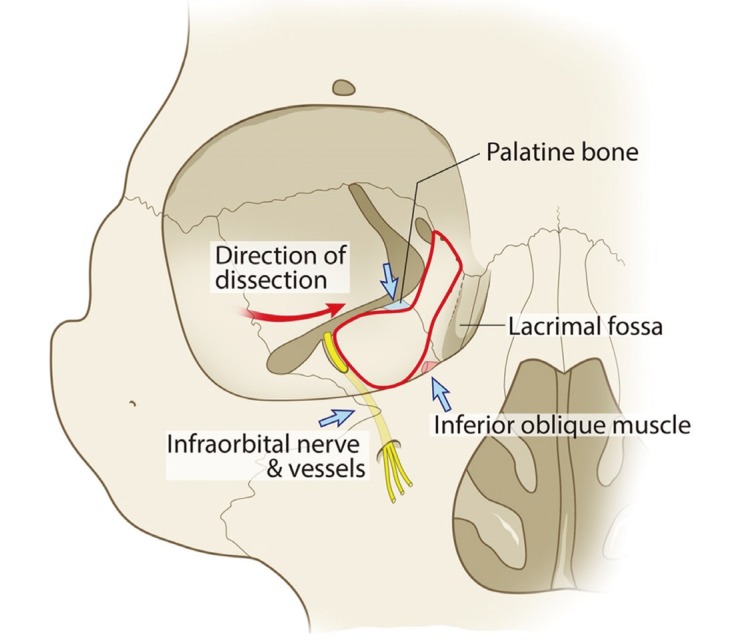
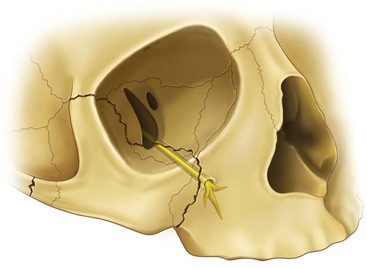
Orbital floor fracture maxillary nerve. If someone has an orbital rim fracture it is likely they have other injuries to the face and possibly the optic nerve. Imaging computed tomography scanning with both axial and coronal views figure 11 is required although studies with newer magnetic resonance imaging mri modalities suggest that in the future this may be the investigation. Palpate for orbital rim fractures and compare facial symmetry to exclude the possibility of an associated malar fracture. The maxillary branch of cranial nerve v exits as the infraorbital nerve providing sensory innervations to the ipsilateral orbital floor mid face and posterior upper gingival.
It is estimated that about 10 of all facial fractures are isolated orbital wall fractures the majority of these being the orbital floor and that 30 40 of. The orbital floor is formed by the roof of the maxillary sinus. Fracture of inferior or medial orbital walls with out fracture of orbital ridge. An orbital blowout fracture is a traumatic deformity of the orbital floor or medial wall typically resulting from impact of a blunt object larger than the orbital aperture or eye socket most commonly the inferior orbital wall i e.
Branches of the external carotid artery supply blood to the face. Approaches to the orbital floor or. 33 are associated with ocular trauma. In 50 of cases.
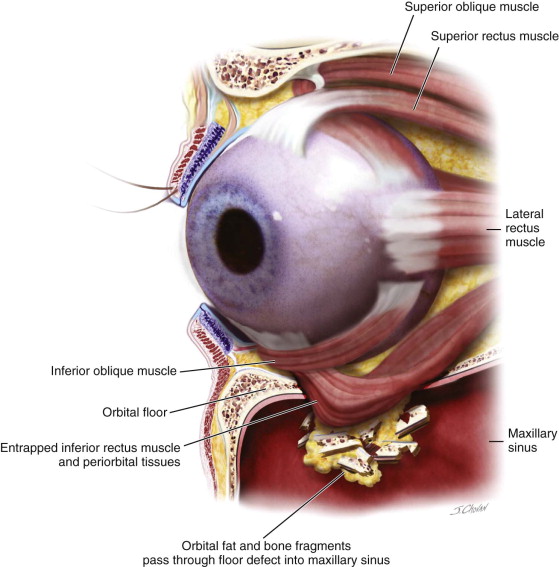
A crack in the very thin bone that makes up these walls can pinch muscles and other structures around the eye keeping the. Infraorbital paraesthesia or anaesthesia can occur when a fracture of the orbital floor affects the infraorbital nerve. Adipose tissue inferior rectus or inferior oblique can entrap within maxillary or ethmoid sinus. A blowout fracture of the orbital floor is defined as a fracture of the orbital floor in which the inferior orbital rim is intact.
The floor is likely to collapse because the bones of the roof and lateral walls are robust. In children the fracture may spring back into place see trapdoor fracture. Cranial nerve v2 sensation. The facial nerve supplies the muscles of facial expression.
Non blow out fracture lateral inferior and superior orbital ridge fracture typically occurs with other facial fractures. These findings occur with large fractures in which the orbital soft tissues prolapse into the maxillary sinus. Fractures of the orbital floor are common. The infraorbital artery a branch of the maxillary artery and the infraorbital vein also are found within the infraorbital groove flanking the infraorbital nerve and.
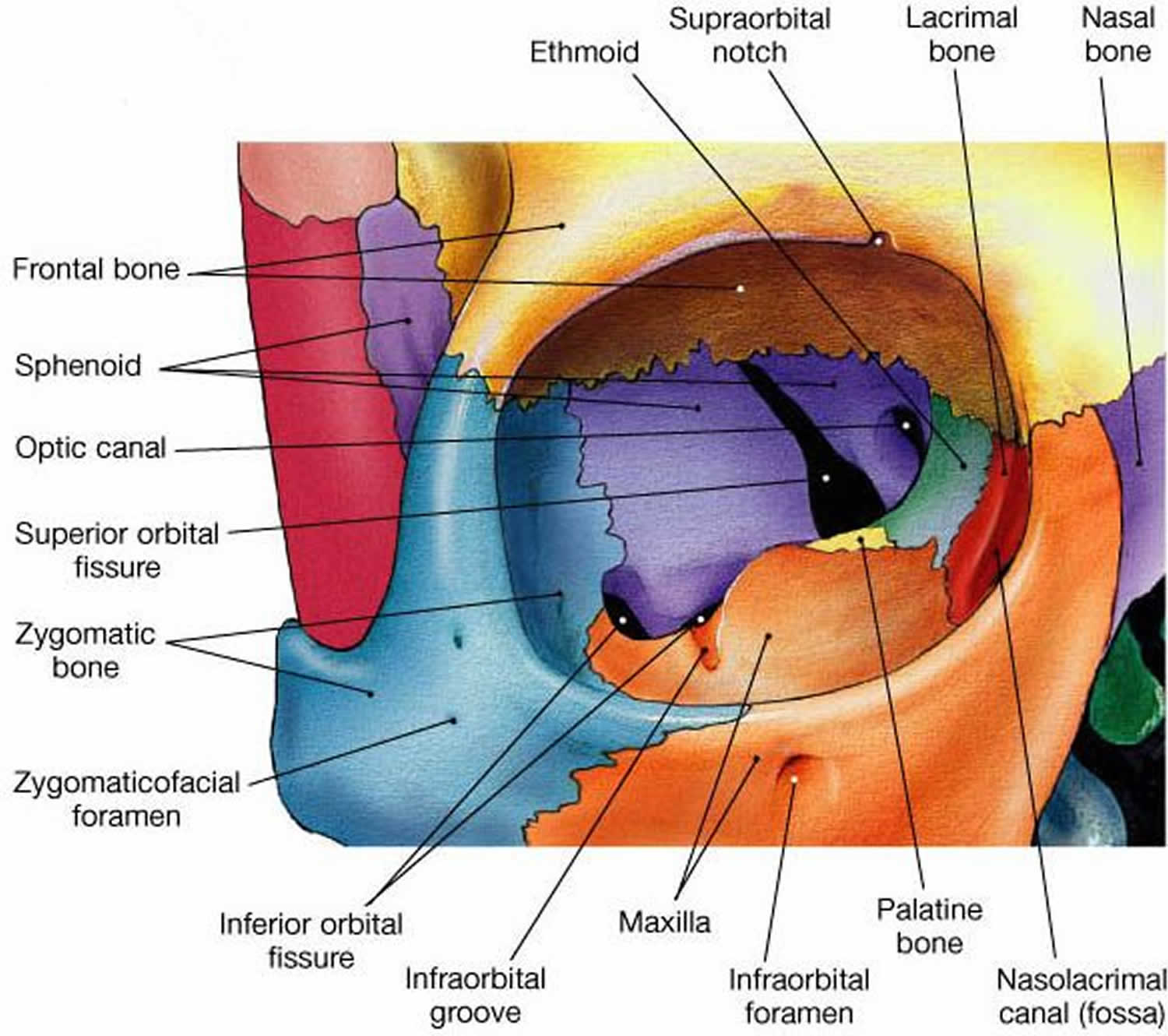
Blood and sensory supply. Without associated orbital rim fracture are. Parts of the sphenoid palatine and ethmoid bones form the apex of the orbit. Most fractures occur in the floor posterior and medial to the infraorbital groove 2.