Orbital Floor Fracture Treatment Emedicine

The weakest portion of the orbit is the thin orbital floor maxilla and the lamina papyracea ethmoid bone medially and inferiorly.
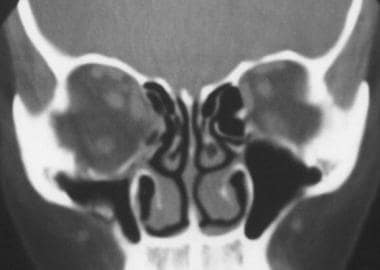
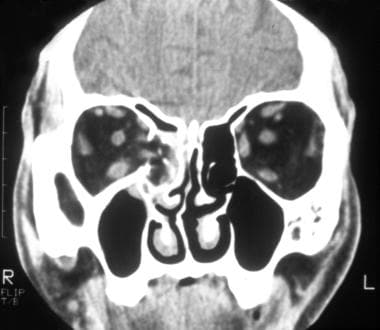
Orbital floor fracture treatment emedicine. A study by coon et al identified 4 indications for surgical intervention in pediatric patients with orbital fractures. Floor fractures may occur in combination with zygomatic arch fractures le fort type ii or iii midface fractures or fractures of other orbital bones. Medical treatment is warranted for patients for whom surgery is not indicated. Large orbital floor fractures ie those with radiologic evidence of significant displacement or comminution of more than 50 of the orbital floor with prolapse of orbital soft tissue that are likely to lead to significant enophthalmos usually reported as 2 mm however a study by vicinanzo et al suggested that in cases of orbital floor.
Orbital fractures were found in 86 of all orbital contusion cases in trauma centers. The inferior orbital nerve courses through the maxilla in the orbital floor. Getting hit with a baseball or a fist often causes a orbital blowout fracture. Treatment for orbital fracture comprises of surgery in severe cases and ice packs rest and antibiotics in mild fractures.
And in 66 7 of patients with fall injuries and open globe diagnoses the result was legal blindness. Orbital fracture is a breakage in the bone in the eye socket which can involve the rim the floor or even both. The globe usually does not rupture and the resultant force is transmitted throughout the orbit causing a fracture of the orbital floor. However the nasal side and the floor of the socket is paper thin in many regions.
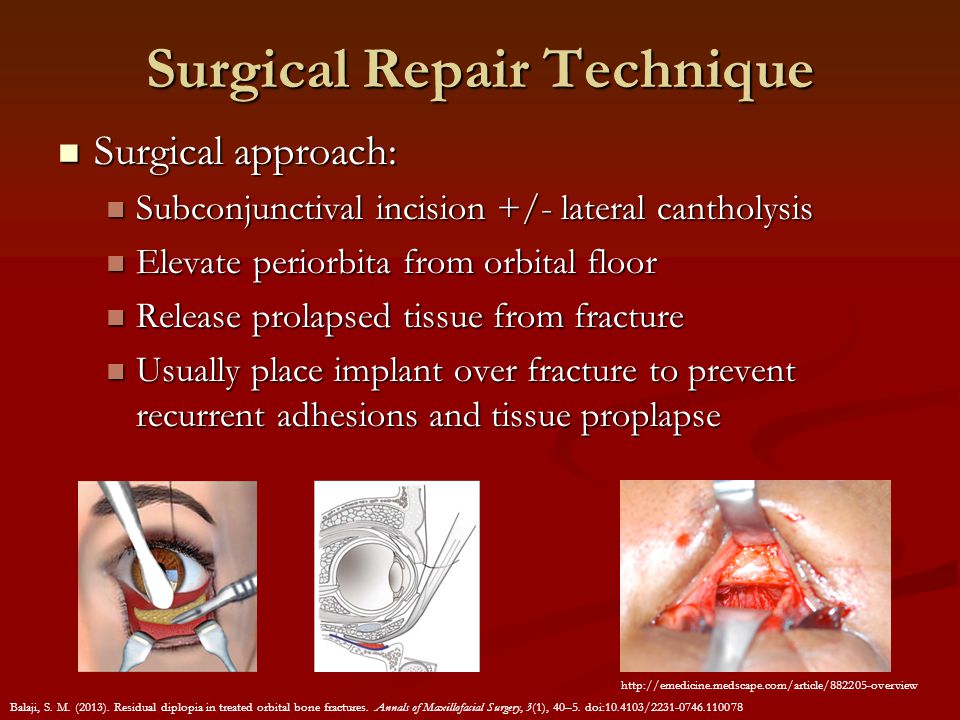
The goal of treatment is to maintain or restore the best possible physiologic function and aesthetic appearance to the area of injury. Orbital floor fractures may result when a blunt object which is of equal or greater diameter than the orbital aperture strikes the eye or on the cheek 1. This approach may be especially useful when repairing a floor fracture of the trap door variety. This may include patients who present without significant enophthalmos 2 mm or more a lack of marked hypo ophthalmos absence of an entrapped muscle or tissue a fracture of less than 50 of the floor or a lack of diplopia.
Facial skeleton fractures can result from low medium or high velocity trauma. A transantral approach allows access to the orbital floor via the maxillary sinus. Orbital floor fractures may result when a blunt object which is of equal or greater diameter than the orbital aperture strikes the eye. Orbital floor fractures may result when a blunt object which is of equal or greater diameter than the orbital aperture strikes the eye.