Oracle Ceil Floor
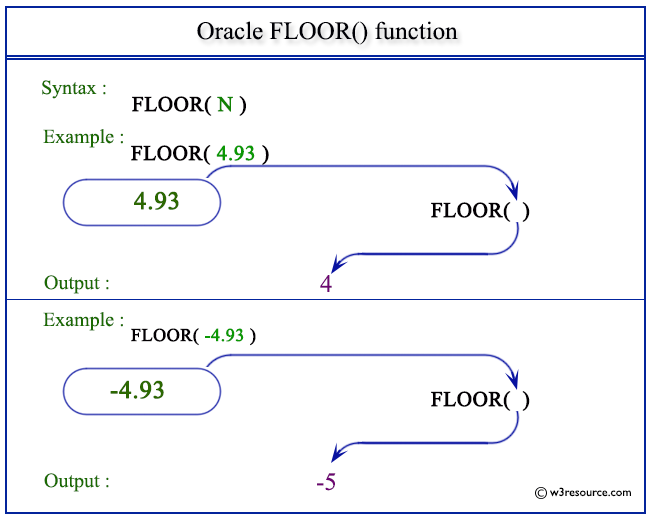
The statement below returns 4 which is the largest integer value of given number 4 93 as specified in the argument.
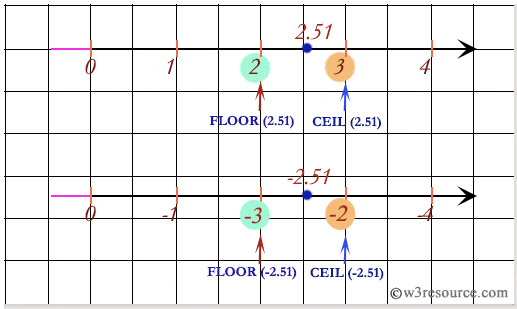
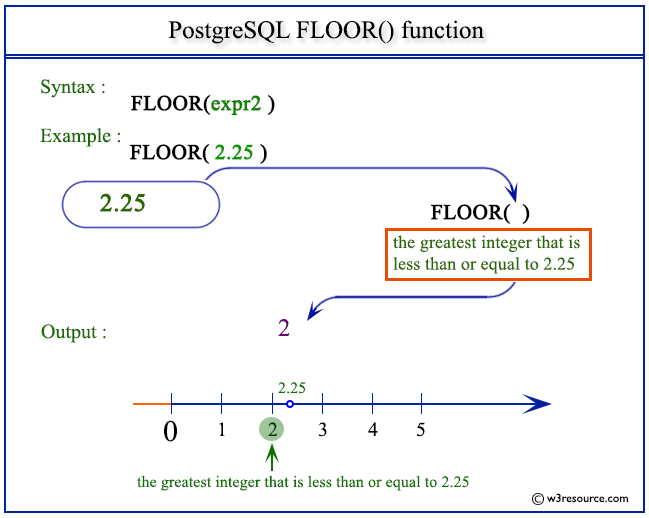
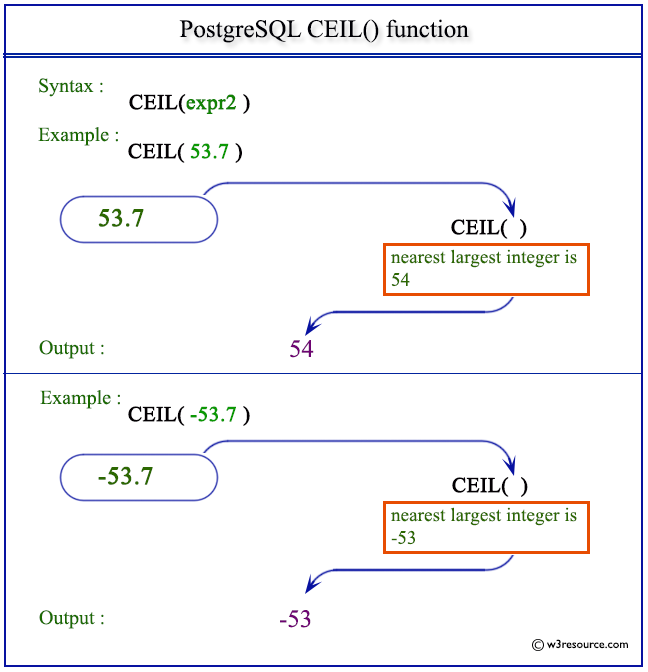
Oracle ceil floor. Description of the illustration ceil gif. The trunc function returns a number truncated to a certain number of decimal places. Select floor 4 93 from dual. Floor 4 93 4 example.
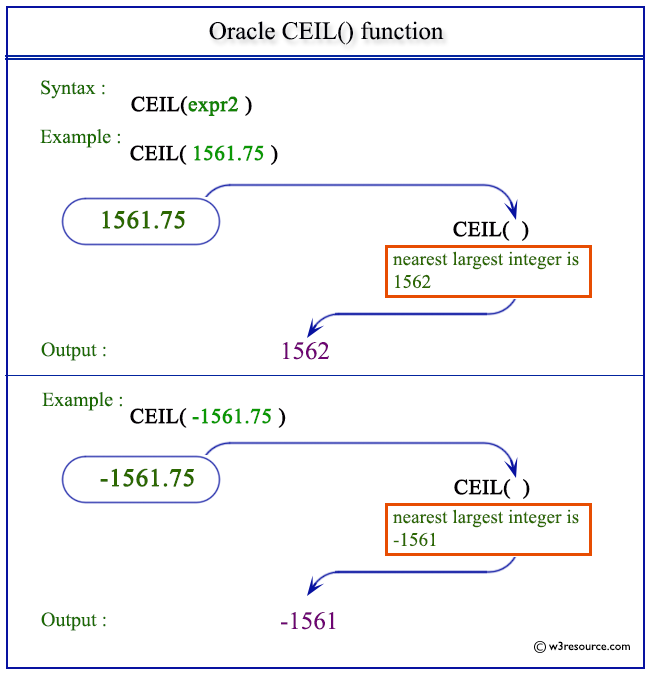
The oracle ceil function and floor function are opposites of each other and are very useful functions when dealing with numbers. Learn what they are and see some examples in this article. This oracle tutorial explains how to use the oracle plsql ceil function with syntax and examples. This function takes as an argument any numeric datatype or any nonnumeric datatype that can be implicitly converted to a numeric datatype.
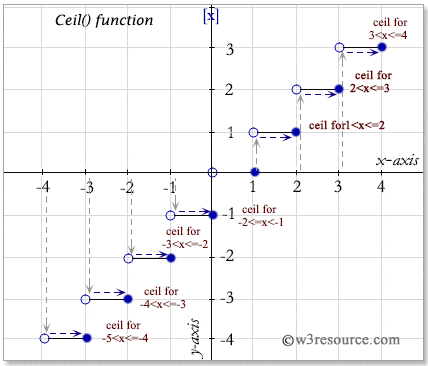
The ceiling function is usually denoted by ceil x or less commonly ceiling x in non apl computer languages that have a notation for this function. Floor with negative value. Round returns n rounded to i places to the right of the decimal point. For ceiling and.
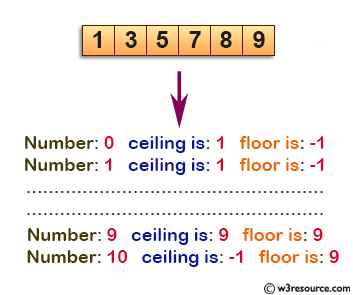
Default value of i is 0. Here is the result. Pictorial presentation of floor function. If the specified number is null the result of these functions is null.
The purpose of the oracle ceil function is to return the smallest integer value greater than or equal to the supplied number. The specified number must be a double precision number. Floor and ceil unlike round and trunc do not take an optional parameter for precision because their output is always an integer. The oracle plsql ceil function returns the smallest integer value that is greater than or equal to a number.
The j programming language a follow on to apl that is designed to use standard keyboard symbols uses. The ceil and ceiling functions round the specified number up and return the smallest number that is greater than or equal to the specified number.